What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the ovary begin to grow and divide in an unregulated way. This is called primary ovariancancer.However, cancer cells gradationally grow into the surrounding tissues, if not caught early. Occasionally the cells can spread beyond the ovary to the womb, abdomen and lungs. The cells also grow in these new places as secondary tumours. When cancer spreads like this, it's called metastasis.
The prevalence of ovarian cancer increases with age. The estimated age-adjusted prevalence varies from0.9 –to 8.4 per woman in various population-based cancer registries in India. There are several types of ovarian cancer. The most common type is epithelial ovarian cancer, which develops from the surface layer of cells in the ovary. This cancer type is rare in adolescent women and is generally found in women who have been through menopause.
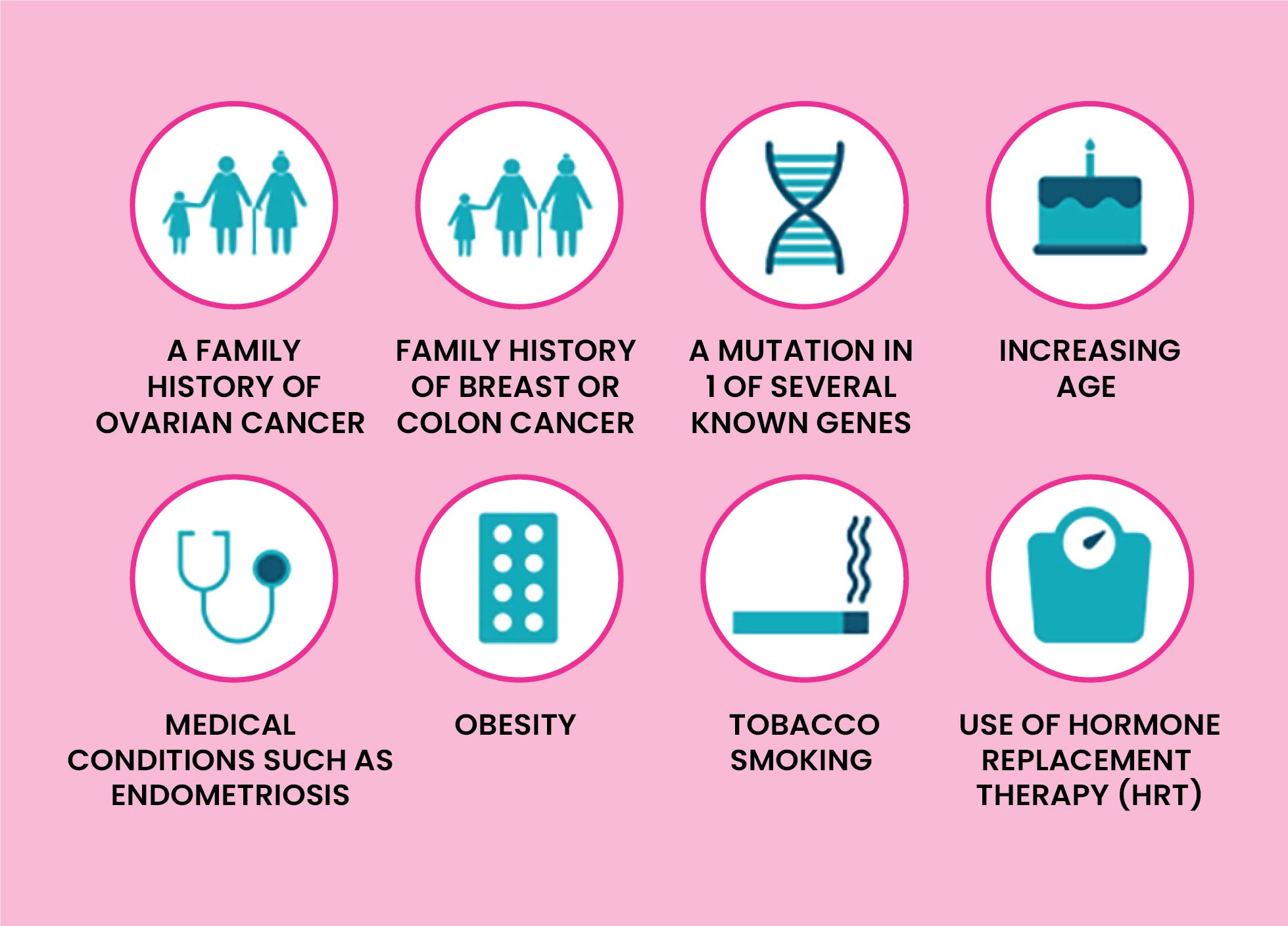
What are the Risk factor of Ovarian Cancer?
In utmost cases, the causes of ovarian cancer are unknown. Still, some risk factors increase the chances of developing ovarian cancer, a few of which are mentioned below.
What are the Types of Ovarian Cancer?
Epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common type of ovarian cancer. Primary peritoneal cancer and fallopian tube cancer are analogous to epithelial ovarian cancer and are treated in the same way. Rare types of ovarian cancer include germ cell tumours, stromal tumours and sarcomas.
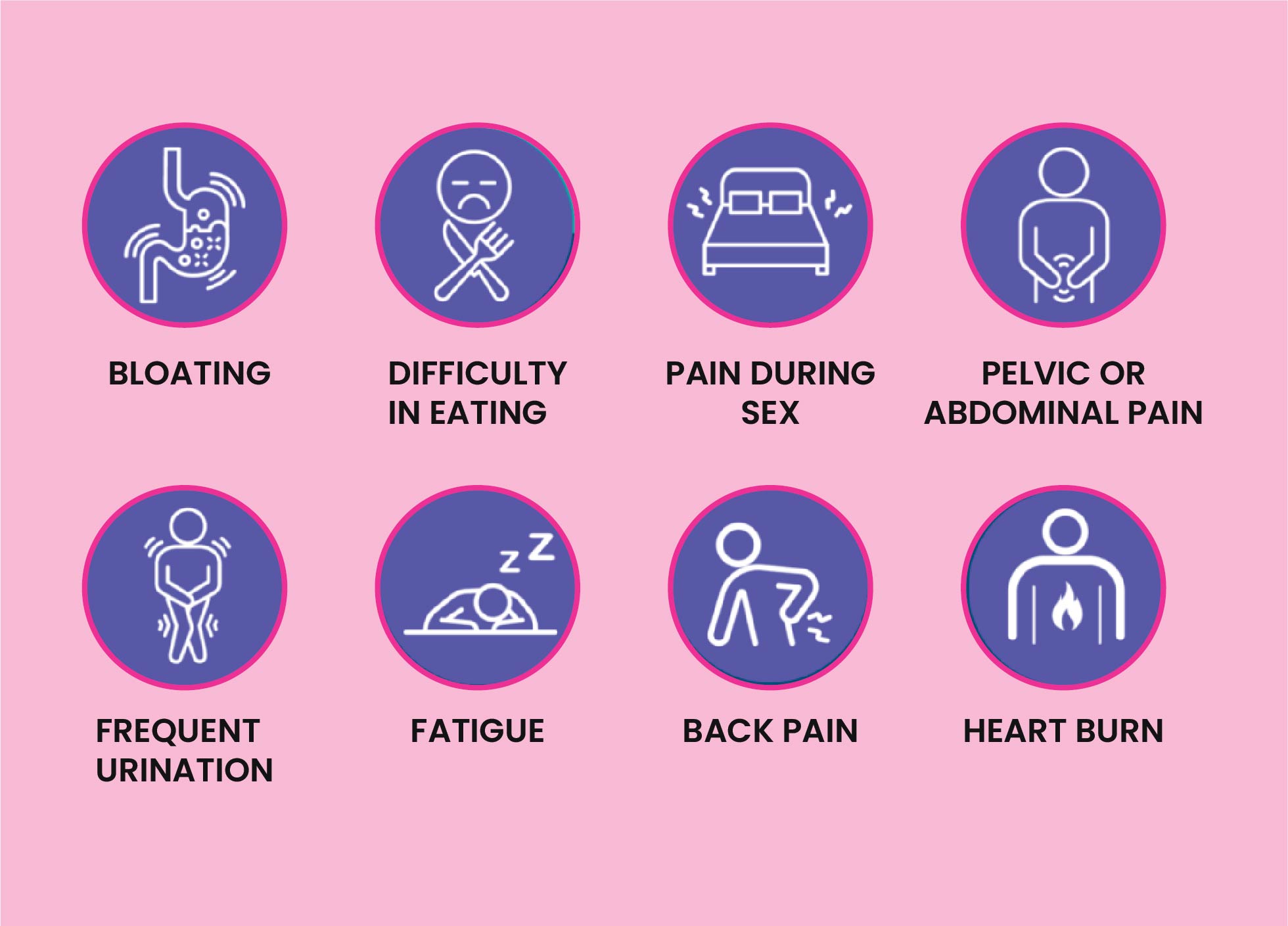
What are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer?
There are very rare symptoms in early-stage ovarian cancer. In the advanced stage, ovarian cancer may cause some signs and symptoms that may include:
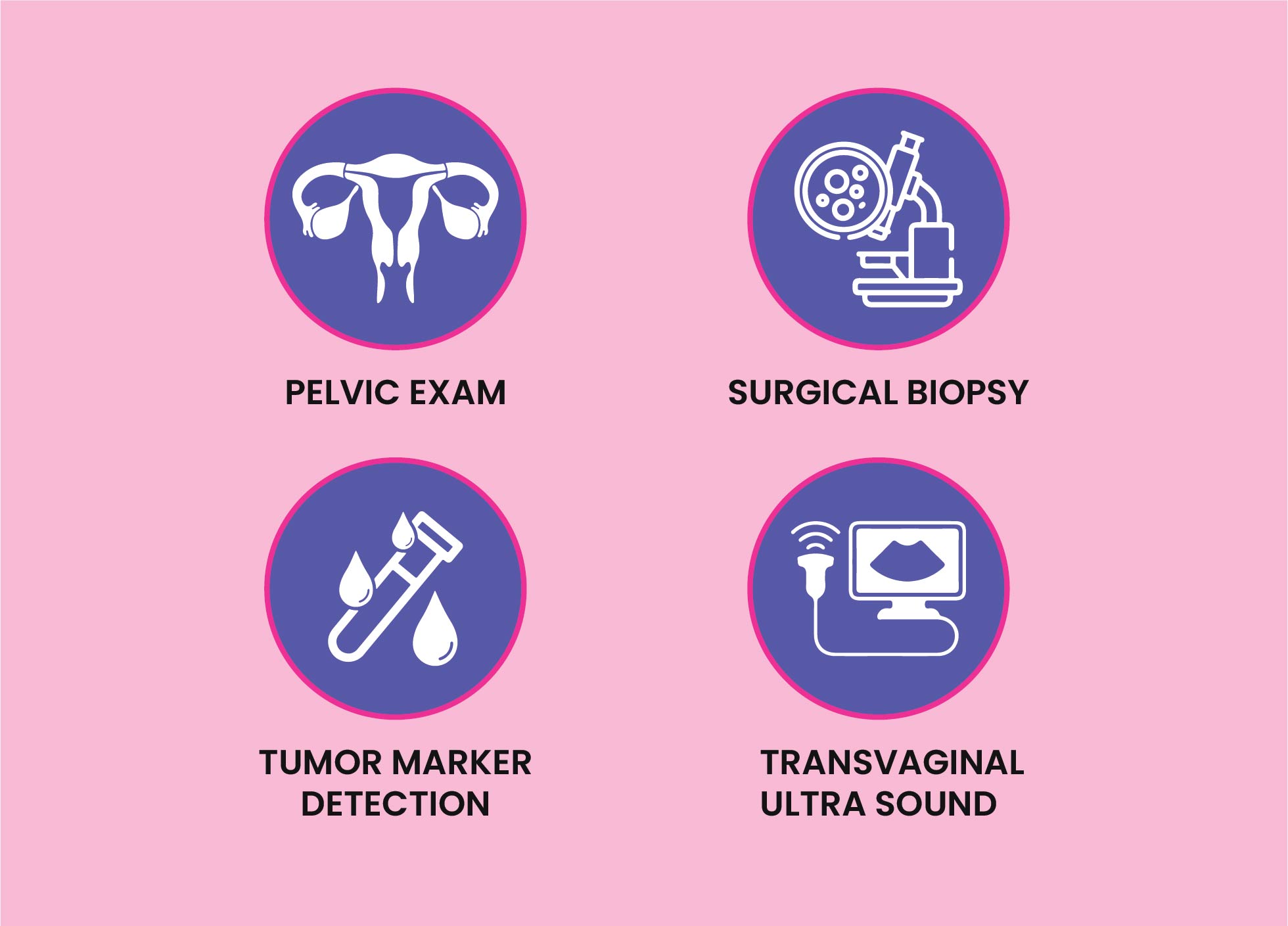
How to Diagnose Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer may be suspected if an ovary appears unusual on an ultrasound checkup. Abnormal blood tests similar to high levels of a protein called CA125 can make it more probable that it's malignant.
You are likely to be offered a CT scan (Computed tomography scan) of your abdomen and pelvis. Occasionally, you may be advised to have a biopsy (the taking of a small sample of tissue for examination). This may be done with you awake in theX-ray department or as a keyhole operation with a general anaesthetic.
If your abdomen is swollen with fluid (called ascites) you may be advised to have this drained. This is generally done under ultrasound guidance. The removed fluid may be checked for cancer cells.
Still, you will be referred to a specialist gynaecology cancer centre to plan treatment, if cancer is verified.
What are the Treatment available for Ovarian Cancer?
Your treatment depends on various factors. These include what type of ovarian cancer you have, how large it is and whether it has spread to other parts or not, what the cancer cells look like under the microscope and your general health. Treatment includes surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and supportive care.
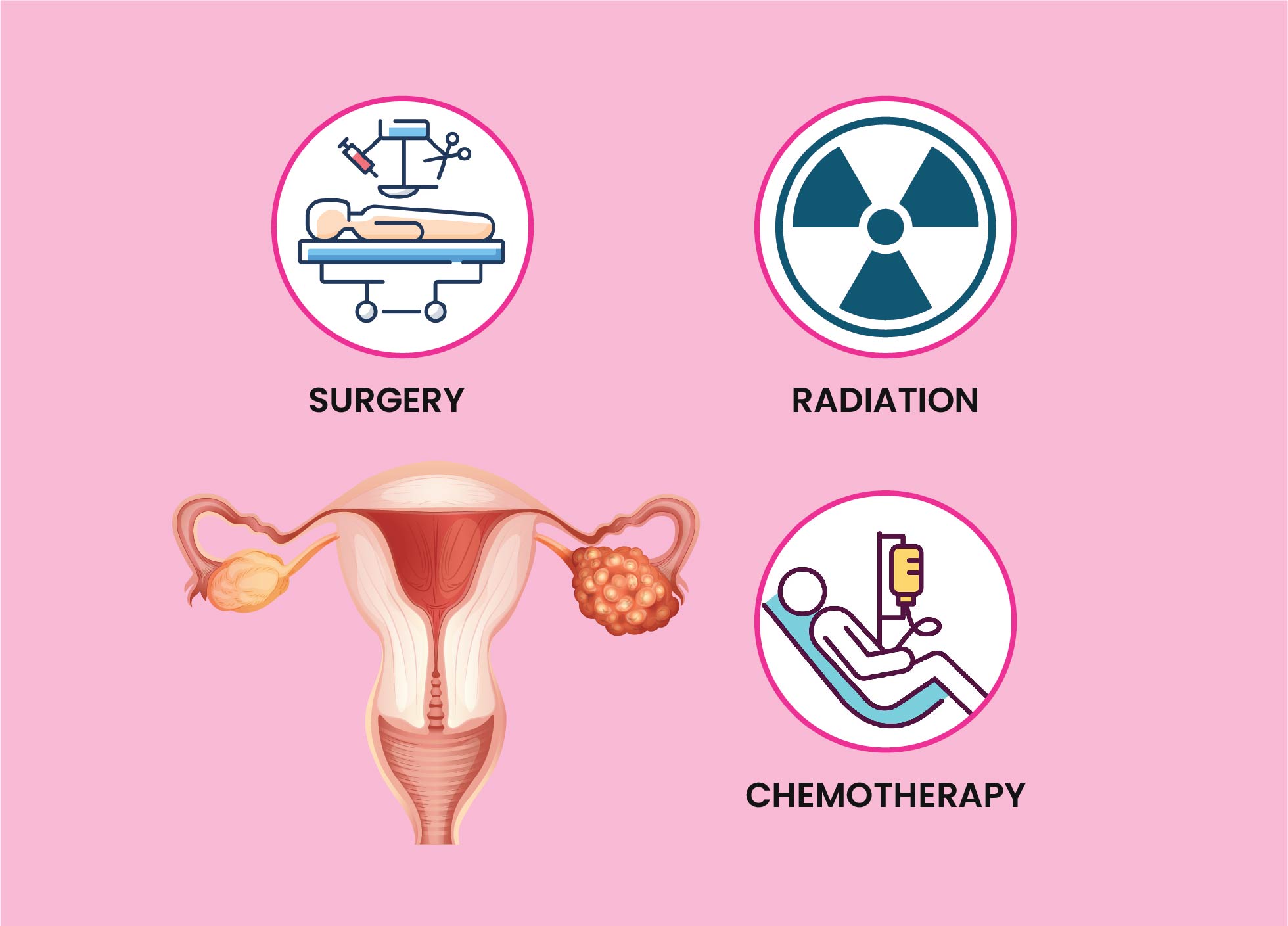
FOLLOW UP
You may not be well enough to have the treatment/ s described above or you may decide againstanti-cancertreatment.However, you should discuss your wishes with your healthcare professionals, if so. You'll be offered treatment to relieve symptoms. This is known as supportive or palliative care.
Busting myths about ovarian cancer
Talcum powder or cosmetics cause ovarian cancer
You may have heard that products containing the mineral talc, like some feminine hygiene powders and mineral cosmetics, cause ovarian cancer. There isn’t any good science showing that talc causes ovarian cancer. Sorry ladies! It’s a myth!
Ovarian cysts can turn into cancer
Cysts rarely turn into cancer, nor do conditions like Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) up your risk of cancer.
The HPV vaccine protects against ovarian cancer
The HPV vaccine protects against the most common strains of the Human Papilloma Virus, which are unrelated to ovarian cancer but it’s still a good vaccine to get, especially for teens, as it protects against cervical cancer.
if you have a family history of ovarian cancer then you are bound to get it
Heredity only accounts for a mere 10 percent of cases. The biggest risk factor for ovarian cancer? Having ovaries! All women need to be aware of ovarian cancer symptoms and go for regular checkups.
It does not affect young women
It’s not true. About 20% of women with ovarian cancer are less than 50 years of age.